hostnamectl set-hostname dev-ipa01.example.org
Установка первой FreeIPA-реплики
1. Подготовка ОС к установке FreeIPA-сервера
-
Проверьте настройки точного времени.
-
Проверьте сетевые настройки.
-
Задайте полное имя хоста. Пример:
-
Добавьте в
/etc/hostsзаписи для локальной, или для всех существующих/будущих IPA-реплик. Пример:192.168.50.21 dev-ipa01.example.org dev-ipa01 192.168.50.22 dev-ipa02.example.org dev-ipa02 192.168.50.23 dev-ipa03.example.org dev-ipa03
-
Перегенерируйте ssh-ключи на тот случай, если машина была получена из единого образа (без автоматический смены ssh-ключей при первом её запуске). Пример:
rm -f /etc/ssh/ssh_host_*_key* systemctl restart sshd
-
Обновите
/etc/machine-id:rm -f /etc/machine-id dbus-uuidgen --ensure=/etc/machine-id
-
Обновите систему.
-
Добавьте в систему пакеты freeipa-server.
-
Перезапустите хост.
2. Установка первого сервера FreeIPA
Установку будем производить в бездиалоговом режиме с заданием всех необходимых опций из командной строки.
2.1. Описание опций установочного скрипта
Описание некоторых опций:
-
--ds-password — задаёт особо секретный пароль аккаунта 'cn=Directory Manager', на основе которого синхронизируются реплики IPA и зашифрован ключ Центра Сертификации. Так-как этой УЗ доступно содержимое всего LDAP-каталога, что позволяет наблюдать содержимое особо секретных веток, то необходимо ограничить известность этого пароля узким кругом лиц.
-
--admin-password — задаёт пароль первого пользовательского аккаунта во FreeIPA, состоящего в группе 'admins', с помощью которого будет произведена первичная настройка FreeIPA. Членам группы 'admins' позволительны все доступные операции, что позволяет нанести необратимый вред установленному экземпляру FreeIPA, поэтому после первичной настройки заблокируем эту УЗ, а доступ к паролю ограничим узким кругом лиц.
-
--ip-address — указывает соновной ip-адрес. Необязательный параметр в случае наличия только одного ip-адреса.
-
--unattended — подавляет все запросы инсталлятора.
-
--setup-dns --no-forwarders — добавляет роль DNS-сервера без настройки форвардеров, которые мы настроим позже, после установки первого контроллера.
-
--auto-reverse --allow-zone-overlap — две опции, которые необходимы для автоматического добавления обратной зоны DNS, в которой находится основной ip-адрес сервера FreeIPA. (https://access.redhat.com/solutions/4237121)
-
--no-hbac-allow — запрещает автоматическое добавление HBAC-правила, которое позволяет всем пользователям домена заходить на все машины домена через ssh.
-
--ntp-server — задаёт ip-адрес NTP-сервера. Адрес будет добавлен в
/etc/chrony.conf. -
--mkhomedir — опция для скрипта ipa-client-install. Скрипт автоматически вызывается из ipa-server-install после поднятия домена и необходим для введения локальной машины в домен FreeIPA. Опция же добавляет в локальную операционную систему PAM-правило, отвечающее за автоматическое создание домашней директории для входящего на эту машину по ssh пользователю.
-
--subject-base — the certificate subject base (default O=<realm-name>).
-
--ca-subject — the CA certificate subject DN (default CN=Certificate Authority,O=<realm-name>).
Ниже показаны различия в именах сертификатах без использования или с использованием этих опций.
CN=Certificate Authority,O=EXAMPLE.ORG
CN=Acme Corp Root CA,O=Acme Corp
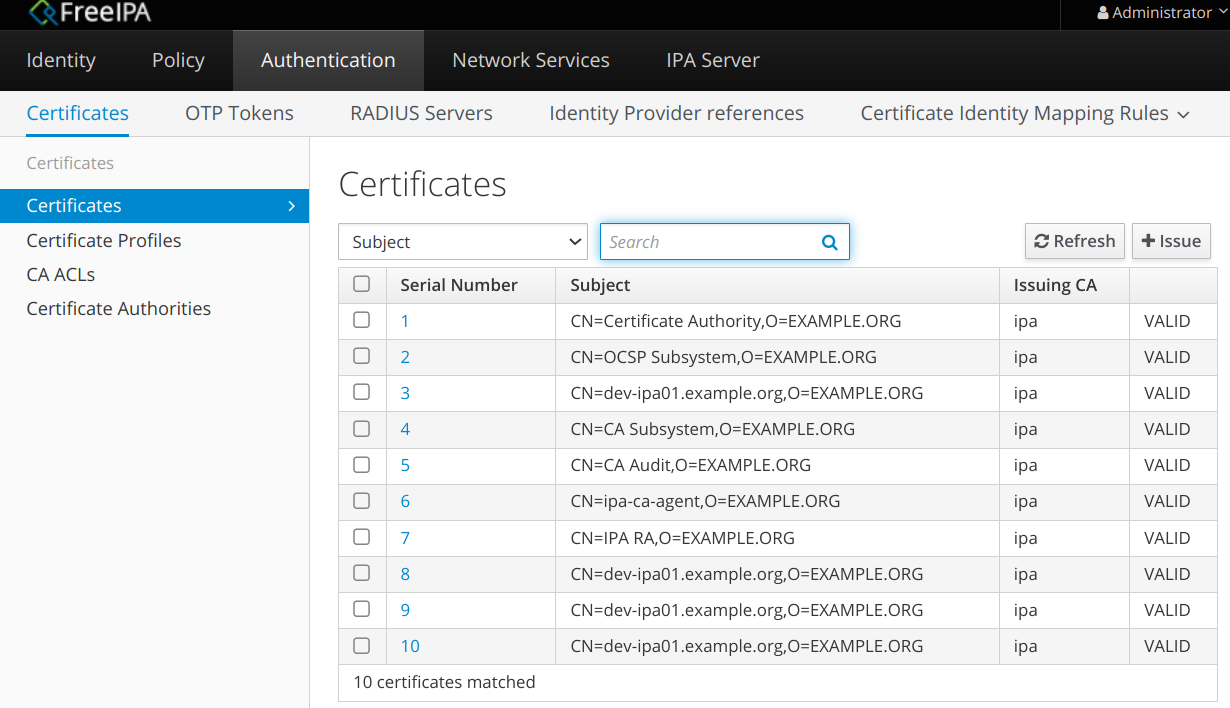
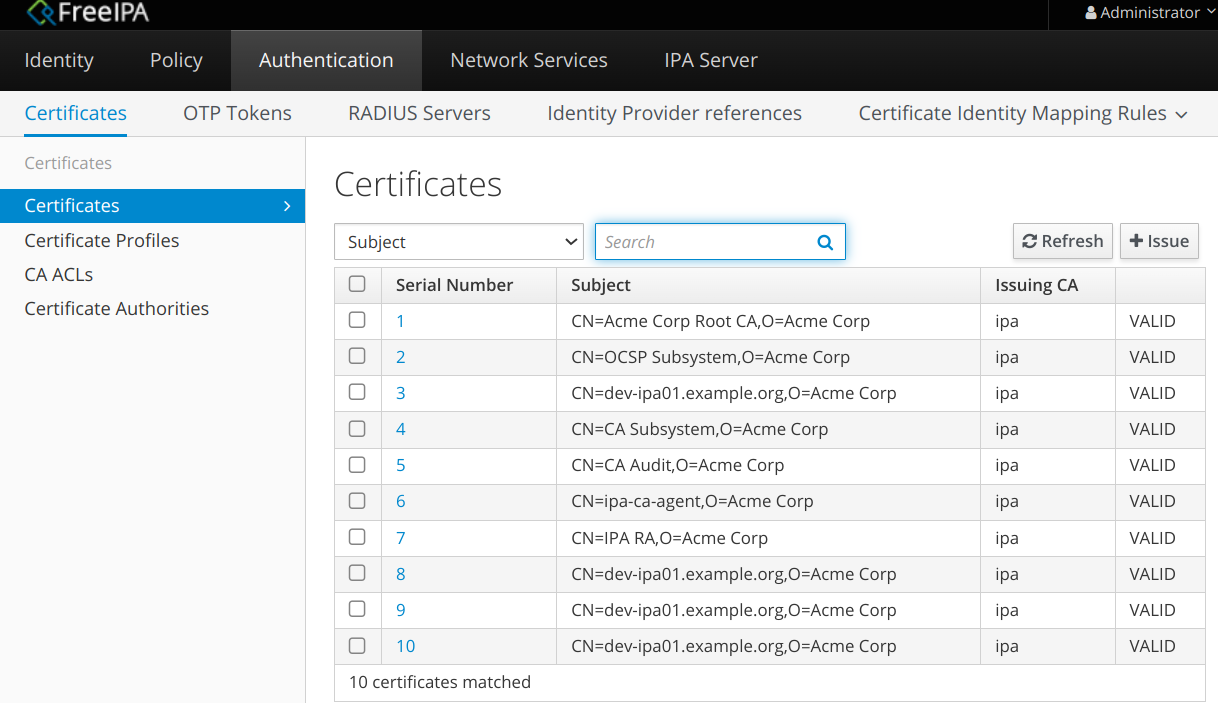
В Chromium стандартный и специально именованный сертификаты отображаются так:
CN=Certificate Authority,O=EXAMPLE.ORG
CN=Acme Corp Root CA,O=Acme Corp

2.2. Правила задания пароля для DM-аккаунта
Судя по исходникам, пароль может содержать все ASCII-символы, кроме обратного слэша (видим следующее присваивание — bad_characters = '\\' — в регулярных выражениях символ обратного слэша обычно обозначается двумя обратными слэшами). Наверное, наравне с обратным слэшем, лучше будет воздержаться от использования одинарных, обратных и двойных кавычек, а также прямого слэша и вертикальной черты.
Для генерации пароля, который не будет включать в себя символы слэшей и кавычек (одинарных, двойных и обратных), проще использовать bash-строку:
tr -dc 'A-Za-z0-9!#$%&()*+,-.:;<=>?@[]^_{}~' </dev/urandom | head -c 43; echo
Код, отвечающий за проверку паролей, можно найти в файле freeipa-${VER}/ipaserver/install/server/install.py. Например для версии ${VER}='4.9.6'`:
def validate_dm_password(password):
if len(password) < 8:
raise ValueError("Password must be at least 8 characters long")
if any(ord(c) < 0x20 for c in password):
raise ValueError("Password must not contain control characters")
if any(ord(c) >= 0x7F for c in password):
raise ValueError("Password must only contain ASCII characters")
# Disallow characters that pkisilent doesn't process properly:
bad_characters = '\\'
if any(c in bad_characters for c in password):
raise ValueError('Password must not contain these characters: %s' %
', '.join('"%s"' % c for c in bad_characters))
# TODO: Check https://fedorahosted.org/389/ticket/47849
# Actual behavior of setup-ds.pl is that it does not accept white
# space characters in password when called interactively but does when
# provided such password in INF file. But it ignores leading and trailing
# whitespaces in INF file.
# Disallow leading/trailing whaitespaces
if password.strip() != password:
raise ValueError('Password must not start or end with whitespace.')
def validate_admin_password(password):
if len(password) < 8:
raise ValueError("Password must be at least 8 characters long")
if any(ord(c) < 0x20 for c in password):
raise ValueError("Password must not contain control characters")
if any(ord(c) >= 0x7F for c in password):
raise ValueError("Password must only contain ASCII characters")
# Disallow characters that pkisilent doesn't process properly:
bad_characters = '\\'
if any(c in bad_characters for c in password):
raise ValueError('Password must not contain these characters: %s' %
', '.join('"%s"' % c for c in bad_characters))
2.3. Процесс установки первого сервера FreeIPA
-
Выполните следующий скрипт и ждите окончания процедуры. В случае наличия на хосте только одного ip-адреса, переменную IP_ADDRESS и опцию '--ip-address' можно не применять.
# Generating new passwords DM_PASSWORD=$(tr -dc 'A-Za-z0-9!#$%&()*+,-.:;<=>?@[]^_{}~' </dev/urandom | head -c 43; echo) ADMIN_PASSWORD=$(tr -dc 'A-Za-z0-9_' </dev/urandom | head -c 14; echo) # Saving new passwords to /root/freeipa_passwords.txt [ -f /root/freeipa_passwords.txt ] && \ mv /root/freeipa_passwords.txt /root/freeipa_passwords.txt.$(date +%y%m%d-%H%M%S) echo -e "${DM_PASSWORD}\n${ADMIN_PASSWORD}" | tee /root/freeipa_passwords.txt IP_ADDRESS="192.168.50.21" DOMAIN_NAME="example.org" CRT_NAME_BASE="Acme Corp" SUBJECT_BASE="O=${CRT_NAME_BASE}" CA_SUBJECT="CN=${CRT_NAME_BASE} Root CA,O=${CRT_NAME_BASE}" ipa-server-install --unattended \ --ds-password=${DM_PASSWORD} --admin-password=${ADMIN_PASSWORD} \ --ip-address=${IP_ADDRESS} --realm=${DOMAIN_NAME^^} \ --setup-dns --no-forwarders --auto-reverse --allow-zone-overlap \ --no-hbac-allow --mkhomedir \ --subject-base="${SUBJECT_BASE}" --ca-subject="${CA_SUBJECT}"stdout:
The log file for this installation can be found in /var/log/ipaserver-install.log ============================================================================== This program will set up the IPA Server. Version 4.12.1 This includes: * Configure a stand-alone CA (dogtag) for certificate management * Configure the NTP client (chronyd) * Create and configure an instance of Directory Server * Create and configure a Kerberos Key Distribution Center (KDC) * Configure Apache (httpd) * Configure DNS (bind) * Configure SID generation * Configure the KDC to enable PKINIT Warning: skipping DNS resolution of host dev-ipa01.example.org The domain name has been determined based on the host name. Checking DNS domain example.org., please wait ... DNS zone example.org. already exists in DNS and is handled by server(s): ['a.iana-servers.net.', 'b.iana-servers.net.'] Please make sure that the domain is properly delegated to this IPA server. Reverse record for IP address 192.168.50.21 already exists Trust is configured but no NetBIOS domain name found, setting it now. The IPA Master Server will be configured with: Hostname: dev-ipa01.example.org IP address(es): 192.168.50.21 Domain name: example.org Realm name: EXAMPLE.ORG The CA will be configured with: Subject DN: CN=Certificate Authority,O=EXAMPLE.ORG Subject base: O=EXAMPLE.ORG Chaining: self-signed BIND DNS server will be configured to serve IPA domain with: Forwarders: No forwarders Forward policy: only Reverse zone(s): No reverse zone Disabled p11-kit-proxy Synchronizing time No SRV records of NTP servers found and no NTP server or pool address was provided. Using default chrony configuration. Attempting to sync time with chronyc. Time synchronization was successful. Configuring directory server (dirsrv). Estimated time: 30 seconds [1/41]: creating directory server instance Validate installation settings ... Create file system structures ... Perform SELinux labeling ... Create database backend: dc=example,dc=org ... Perform post-installation tasks ... [2/41]: adding default schema [3/41]: enabling memberof plugin [4/41]: enabling winsync plugin [5/41]: configure password logging [6/41]: configuring replication version plugin [7/41]: enabling IPA enrollment plugin [8/41]: configuring uniqueness plugin [9/41]: configuring uuid plugin [10/41]: configuring modrdn plugin [11/41]: configuring DNS plugin [12/41]: enabling entryUSN plugin [13/41]: configuring lockout plugin [14/41]: configuring graceperiod plugin [15/41]: configuring topology plugin [16/41]: creating indices [17/41]: enabling referential integrity plugin [18/41]: configuring certmap.conf [19/41]: configure new location for managed entries [20/41]: configure dirsrv ccache and keytab [21/41]: enabling SASL mapping fallback [22/41]: restarting directory server [23/41]: adding sasl mappings to the directory [24/41]: adding default layout [25/41]: adding delegation layout [26/41]: creating container for managed entries [27/41]: configuring user private groups [28/41]: configuring netgroups from hostgroups [29/41]: creating default Sudo bind user [30/41]: creating default Auto Member layout [31/41]: adding range check plugin [32/41]: adding entries for topology management [33/41]: initializing group membership [34/41]: adding master entry [35/41]: initializing domain level [36/41]: configuring Posix uid/gid generation [37/41]: adding replication acis [38/41]: activating sidgen plugin [39/41]: activating extdom plugin [40/41]: configuring directory to start on boot [41/41]: restarting directory server Done configuring directory server (dirsrv). Configuring Kerberos KDC (krb5kdc) [1/11]: adding kerberos container to the directory [2/11]: configuring KDC [3/11]: initialize kerberos container [4/11]: adding default ACIs [5/11]: creating a keytab for the directory [6/11]: creating a keytab for the machine [7/11]: adding the password extension to the directory [8/11]: creating anonymous principal [9/11]: starting the KDC [10/11]: configuring KDC to start on boot [11/11]: enable PAC ticket signature support Done configuring Kerberos KDC (krb5kdc). Configuring kadmin [1/2]: starting kadmin [2/2]: configuring kadmin to start on boot Done configuring kadmin. Configuring ipa-custodia [1/5]: Making sure custodia container exists [2/5]: Generating ipa-custodia config file [3/5]: Generating ipa-custodia keys [4/5]: starting ipa-custodia [5/5]: configuring ipa-custodia to start on boot Done configuring ipa-custodia. Configuring certificate server (pki-tomcatd). Estimated time: 3 minutes [1/32]: configuring certificate server instance [2/32]: stopping certificate server instance to update CS.cfg [3/32]: backing up CS.cfg [4/32]: Add ipa-pki-wait-running [5/32]: secure AJP connector [6/32]: reindex attributes [7/32]: exporting Dogtag certificate store pin [8/32]: disabling nonces [9/32]: set up CRL publishing [10/32]: enable PKIX certificate path discovery and validation [11/32]: authorizing RA to modify profiles [12/32]: authorizing RA to manage lightweight CAs [13/32]: Ensure lightweight CAs container exists [14/32]: Enable lightweight CA monitor [15/32]: Ensuring backward compatibility [16/32]: starting certificate server instance [17/32]: configure certmonger for renewals [18/32]: requesting RA certificate from CA [19/32]: publishing the CA certificate [20/32]: adding RA agent as a trusted user [21/32]: configure certificate renewals [22/32]: Configure HTTP to proxy connections [23/32]: updating IPA configuration [24/32]: enabling CA instance [25/32]: importing IPA certificate profiles [26/32]: migrating certificate profiles to LDAP [27/32]: adding default CA ACL [28/32]: adding 'ipa' CA entry [29/32]: Recording random serial number state [30/32]: Recording HSM configuration state [31/32]: configuring certmonger renewal for lightweight CAs [32/32]: deploying ACME service Done configuring certificate server (pki-tomcatd). Configuring directory server (dirsrv) [1/3]: configuring TLS for DS instance [2/3]: adding CA certificate entry [3/3]: restarting directory server Done configuring directory server (dirsrv). Configuring ipa-otpd [1/2]: starting ipa-otpd [2/2]: configuring ipa-otpd to start on boot Done configuring ipa-otpd. Configuring the web interface (httpd) [1/22]: stopping httpd [2/22]: backing up ssl.conf [3/22]: disabling nss.conf [4/22]: configuring mod_ssl certificate paths [5/22]: setting mod_ssl protocol list [6/22]: configuring mod_ssl log directory [7/22]: disabling mod_ssl OCSP [8/22]: adding URL rewriting rules [9/22]: configuring httpd [10/22]: setting up httpd keytab [11/22]: configuring Gssproxy [12/22]: setting up ssl [13/22]: configure certmonger for renewals [14/22]: publish CA cert [15/22]: clean up any existing httpd ccaches [16/22]: enable ccache sweep [17/22]: configuring SELinux for httpd [18/22]: create KDC proxy config [19/22]: enable KDC proxy [20/22]: starting httpd [21/22]: configuring httpd to start on boot [22/22]: enabling oddjobd Done configuring the web interface (httpd). Configuring Kerberos KDC (krb5kdc) [1/1]: installing X509 Certificate for PKINIT Done configuring Kerberos KDC (krb5kdc). Applying LDAP updates Upgrading IPA:. Estimated time: 1 minute 30 seconds [1/10]: stopping directory server [2/10]: saving configuration [3/10]: disabling listeners [4/10]: enabling DS global lock [5/10]: disabling Schema Compat [6/10]: starting directory server [7/10]: upgrading server [8/10]: stopping directory server [9/10]: restoring configuration [10/10]: starting directory server Done. Restarting the KDC dnssec-validation yes Configuring DNS (named) [1/12]: generating rndc key file [2/12]: adding DNS container [3/12]: setting up our zone [4/12]: setting up our own record [5/12]: setting up records for other masters [6/12]: adding NS record to the zones [7/12]: setting up kerberos principal [8/12]: setting up LDAPI autobind [9/12]: setting up named.conf created new /etc/named.conf created named user config '/etc/named/ipa-ext.conf' created named user config '/etc/named/ipa-options-ext.conf' created named user config '/etc/named/ipa-logging-ext.conf' [10/12]: setting up server configuration [11/12]: configuring named to start on boot [12/12]: changing resolv.conf to point to ourselves Done configuring DNS (named). Restarting the web server to pick up resolv.conf changes Configuring DNS key synchronization service (ipa-dnskeysyncd) [1/7]: checking status [2/7]: setting up bind-dyndb-ldap working directory [3/7]: setting up kerberos principal [4/7]: setting up SoftHSM [5/7]: adding DNSSEC containers [6/7]: creating replica keys [7/7]: configuring ipa-dnskeysyncd to start on boot Done configuring DNS key synchronization service (ipa-dnskeysyncd). Restarting ipa-dnskeysyncd Restarting named Updating DNS system records Configuring SID generation [1/8]: adding RID bases [2/8]: creating samba domain object [3/8]: adding admin(group) SIDs [4/8]: updating Kerberos config 'dns_lookup_kdc' already set to 'true', nothing to do. [5/8]: activating sidgen task [6/8]: restarting Directory Server to take MS PAC and LDAP plugins changes into account [7/8]: adding fallback group [8/8]: adding SIDs to existing users and groups This step may take considerable amount of time, please wait.. Done. Configuring client side components This program will set up IPA client. Version 4.12.1 Using existing certificate '/etc/ipa/ca.crt'. Client hostname: dev-ipa01.example.org Realm: EXAMPLE.ORG DNS Domain: example.org IPA Server: dev-ipa01.example.org BaseDN: dc=example,dc=org Configured /etc/sssd/sssd.conf Systemwide CA database updated. Adding SSH public key from /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ecdsa_key.pub Adding SSH public key from /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ed25519_key.pub Adding SSH public key from /etc/ssh/ssh_host_rsa_key.pub SSSD enabled Configured /etc/openldap/ldap.conf Configured /etc/ssh/ssh_config Configured /etc/ssh/sshd_config.d/04-ipa.conf Configuring example.org as NIS domain. Client configuration complete. The ipa-client-install command was successful ============================================================================== Setup complete Next steps: 1. You must make sure these network ports are open: TCP Ports: * 80, 443: HTTP/HTTPS * 389, 636: LDAP/LDAPS * 88, 464: kerberos * 53: bind UDP Ports: * 88, 464: kerberos * 53: bind * 123: ntp 2. You can now obtain a kerberos ticket using the command: 'kinit admin' This ticket will allow you to use the IPA tools (e.g., ipa user-add) and the web user interface. Be sure to back up the CA certificates stored in /root/cacert.p12 These files are required to create replicas. The password for these files is the Directory Manager password The ipa-server-install command was successful
2.4. Вход в Web UI FreeIPA
-
Пока отсутствует DNS resolving для нового домена example.org, добавьте на свою рабочую машину в файл
/etc/hostsзапись для FreeIPA-сервера:echo "192.168.50.21 dev-ipa01.example.org" >> /etc/hosts
-
Теперь откройте WEB UI страницу FreeIPA-сервера по адресу 'https://dev-ipa01.example.org' и зайдите в консоль управления под учётными данными аккаунта 'admin':
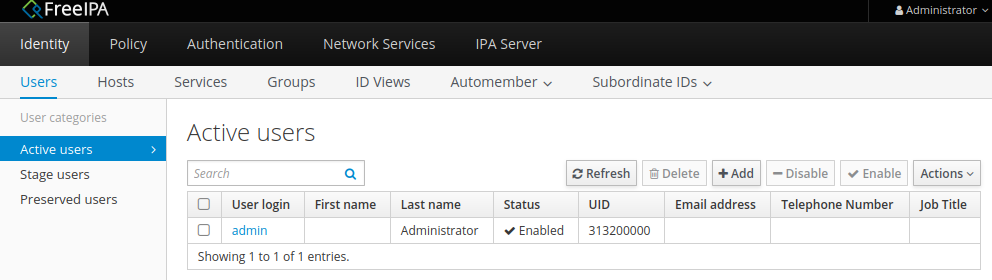
-
Если необходимо добавить CA-сертификат нового домена example.org в "надёжные" своего web-браузера, то сам CA-сертификат скачайте здесь под первым серийным номером:
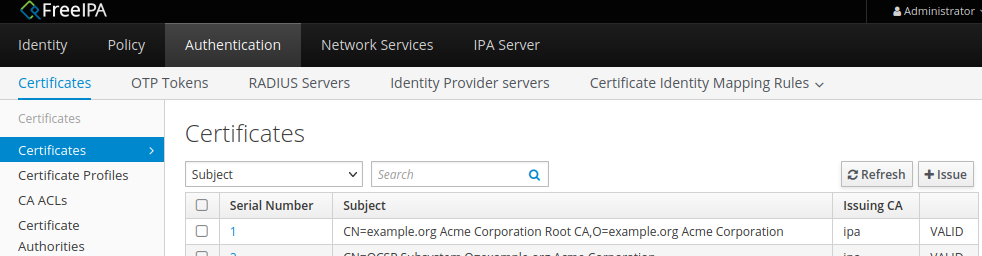
3. Бэкап важной особо секретной информации
-
После первого поднятия домена необходимо сохранить следующую важную информацию в безопасном месте с ограниченным доступом:
-
Пароль аккаунта 'cn=Directory Manager'. Находится в первой строке файла
/root/freeipa_passwords.txt. -
Пароль аккаунта 'uid=admin,cn=users,cn=accounts,dc=example,dc=org'. Находится в второй строке файла
/root/freeipa_passwords.txt. -
Файл
/root/cacert.p12с приватным ключом и сертификатом от Центра Сертификации. Файл зашифрован на основе пароля от 'cn=Directory Manager.
-
-
Перед удалением файла
/root/freeipa_passwords.txt, проверяем корректность сохранённых паролей путём их ввода в ответ на запрос пароля следующих двух команд:kdestroy && kinit admin Password for admin@EXAMPLE.ORG: ********* Ticket cache: KCM:0 Default principal: admin@EXAMPLE.ORG Valid starting Expires Service principal 08/03/2024 23:15:35 08/04/2024 23:13:39 krbtgt/EXAMPLE.ORG@EXAMPLE.ORG
ldapsearch -D 'cn=Directory Manager' -W | head Enter LDAP Password: ********* # extended LDIF # # LDAPv3 # base <dc=example,dc=org> (default) with scope subtree # filter: (objectclass=*) # requesting: ALL # # example.org dn: dc=example,dc=org
-
Сохранив и проверив пароли для УЗ 'cn=Directory Manager' и 'uid=admin' в надёжном месте, удаляем файл
/root/freeipa_passwords.txt:shred -u /root/freeipa_passwords.txt
Напомню, что безопасное удаление с помощью утилиты 'shred' может быть обратимо, например, на журналируемых файловых системах. Поэтому в некоторых случаях необходимо переработать данный сценарий установки FreeIPA-сервера, где пароли бы не сохранялись в файл на жёсткий диск.
4. Проверка корректности установки первой реплики FreeIPA
-
Для проверки работоспособности реплики FreeIPA запустите из командной строки python-утилиту
ipa-healthcheck.ipa-healthcheck --output-type=human
stdout:config file /etc/ipahealthcheck/ipahealthcheck.conf does not exist, using defaults No issues found.
-
Все проверки пройдены успешно.